

 |
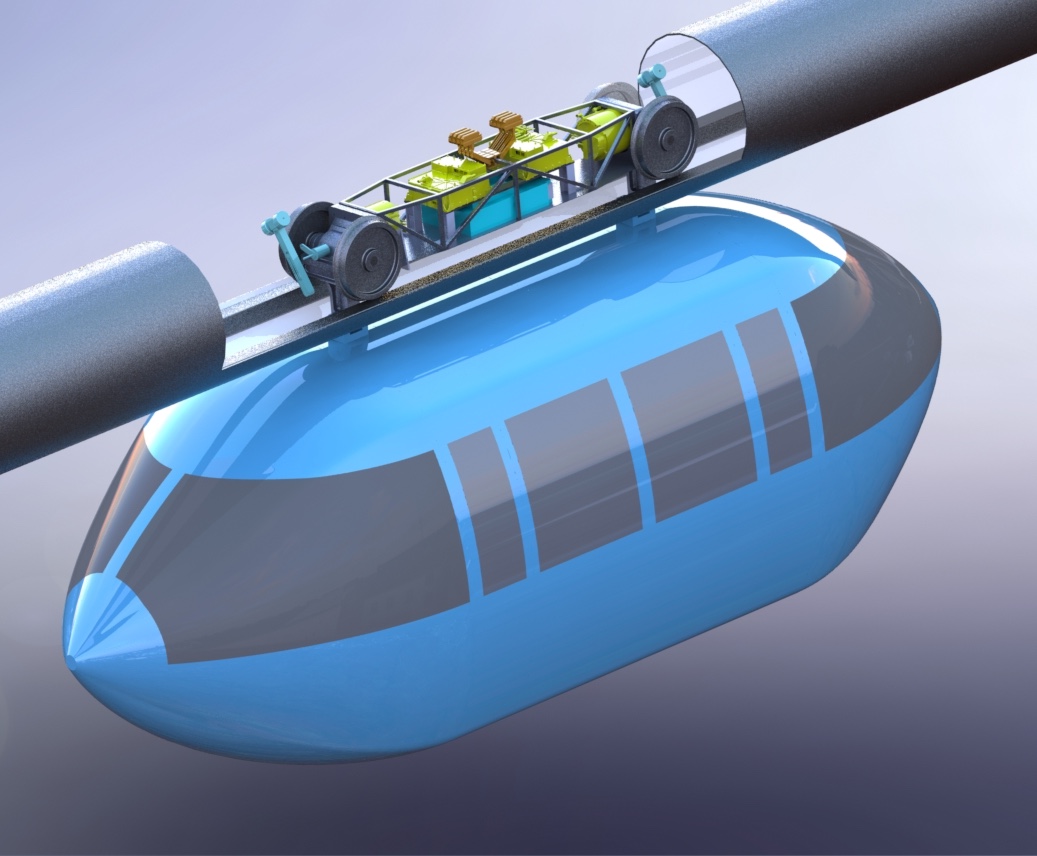
Swift's expertise is in smart, electric drive bogies and proprietary network control protocols. The smart bogies transport the coaches throughout the network of guideways, while the control software directs their movements. The smart bogies are self-contained units that manage their own systems and also the systems in the coaches. Each bogie has enough stored energy and intelligence on-board to complete a route without any external input.Although the bogies are not autonomous, they are very smart and only need a limited amount of directions from the central computer. The network control protocol simply directs the bogies on where, how and when to arrive at its destination, and the bogie handles the rest. The network controller also handles the human inputs and requests, fare-box and other passenger-side communications. A unique attribute of the Swift technologies is switchless junctions. The Swift bogie is actually capable of steering through a junction. The three benefits to a switchless junction are 1) lower guideway maintenance, 2) decreased safety concerns and 3) faster throughput of bogies at each junction. |
The smart bogie is the core of the Swift system. Each bogie carries a passenger or cargo coach. The on-board computer, known as Pan, controls the vehicles' movement, communications with the Prime computer, and safety systems. The bogies are rapid charged at each stop. An important feature of the bogie is its steering system, which allows the bogie to steer through junctions.
Maximum gross weight: 5 metric tonnes for the bogie and loaded coach. | 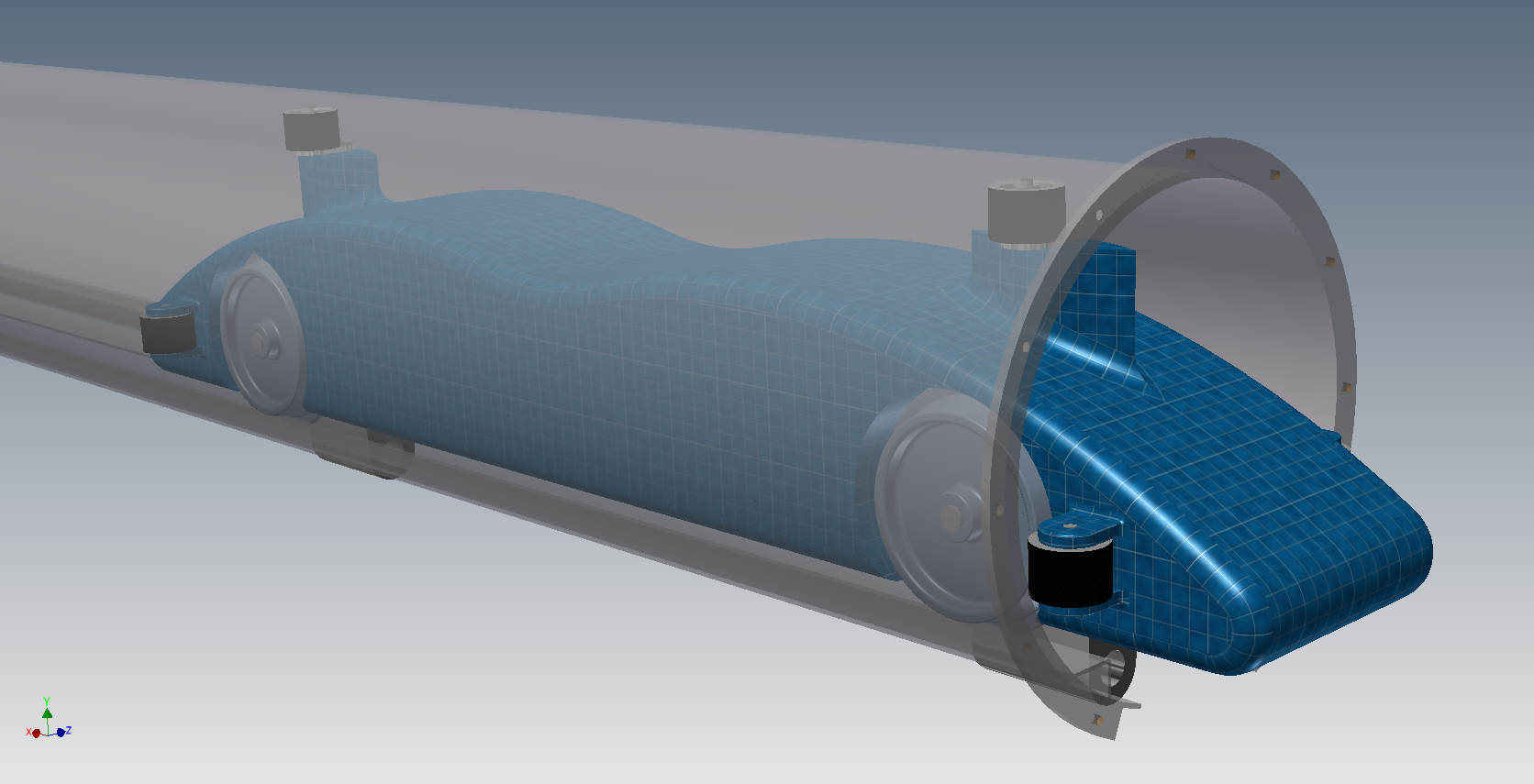 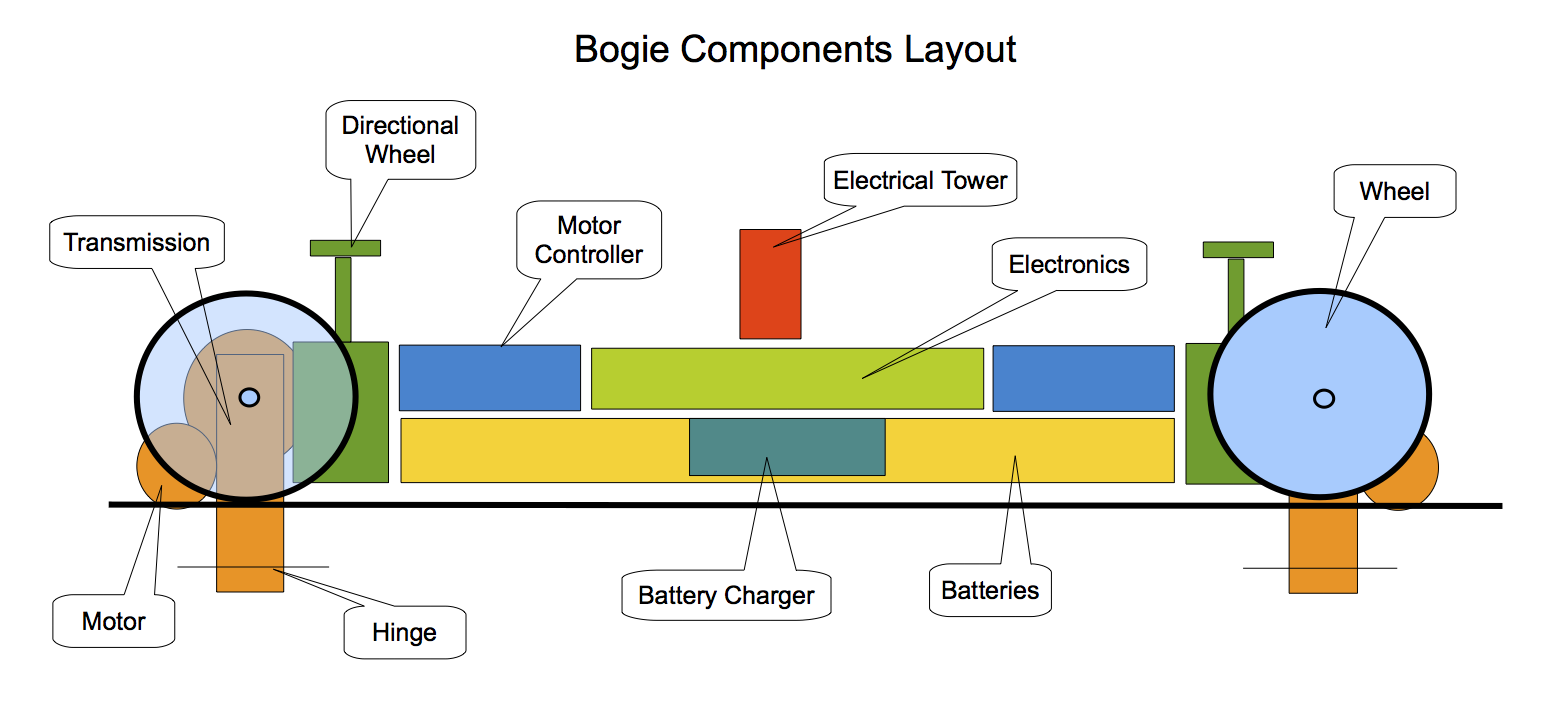 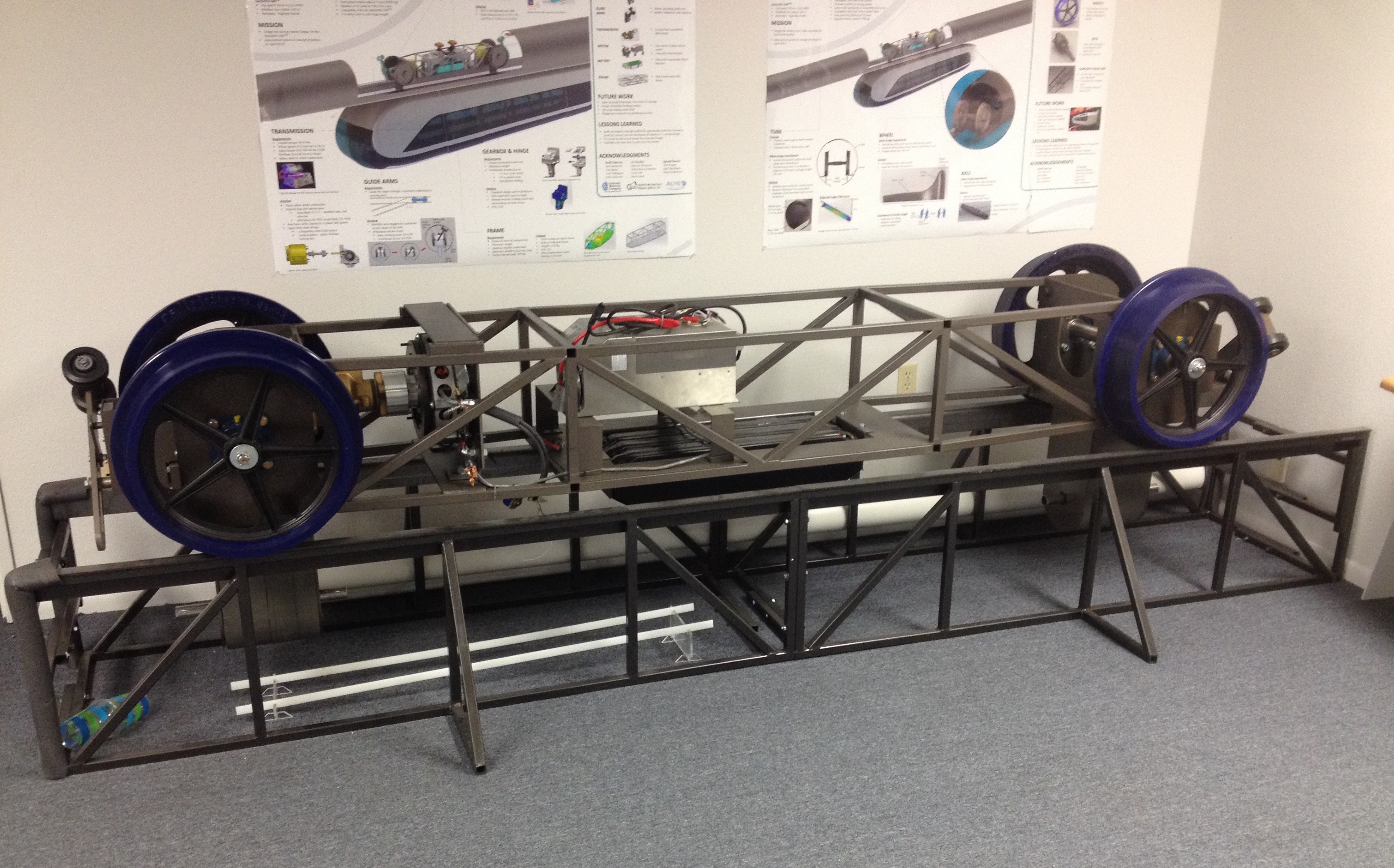 |
 |
The primary network control computer, known as Prime, manages the movement of vehicles throughout the network, and interfaces with the customer and operations side. Prime's routine functions include passenger requests, supervisors mode selections, any special requests and modifications to prior orders. Prime directs the bogies by communicating with the Pan computer on each bogie. Pan receives orders from Prime through several channels and takes actions to complete its assigned mission.Each Pan is in constant communications with the other local Pans. The local Pans use their local-area Pan network to coordinate their actions and ensure safe travels of each bogie. Pans take into account local environmental conditions and share this information as part of their group coordinations. |
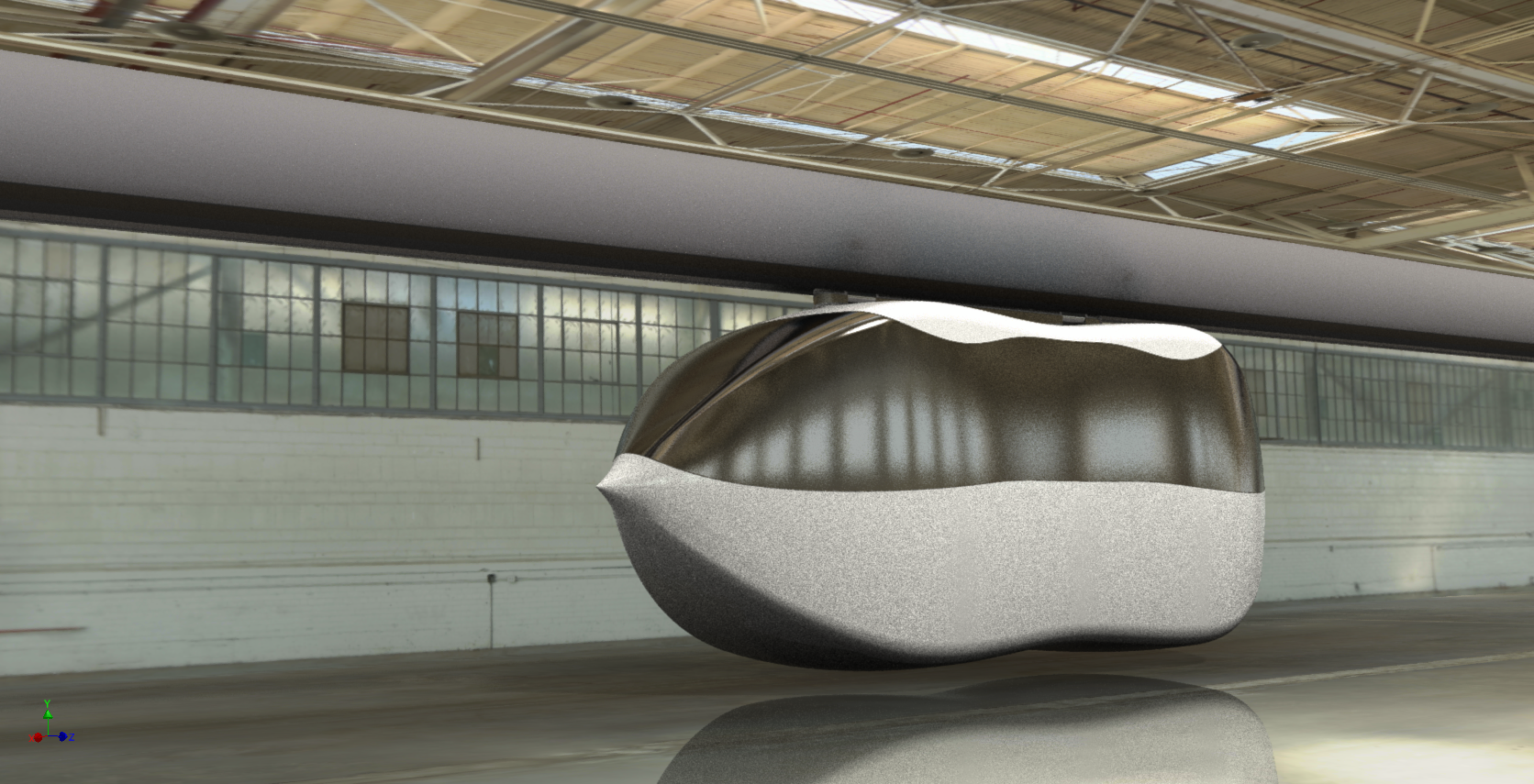
The coaches are custom designed, based on a common template, to meet the needs of each property. The coaches can carry either people or freight, or a combination of the two. Options include emergency evacuation means, number and sizes of doors, HVAC, amount and location of glazings, and seating arrangements, to name a few. The bodies of the coaches can be composite, hybrid composite over steel, or all steel and aluminum. In some cases the coaches can be manufactured locally, or supplied by one of Swift's known suppliers.The coaches have a maximum size and weight, although they can be smaller if needed. Single person pods, or medium-size equipment carriers, or open-framed sightseeing platforms are all possibilities.
Maximum width: 2.5 meters (8.2 feet) |
 |